Understanding of VOC Testing
What are VOCs?
Volatile Organic Compounds are a wide grouping, or large groupings of organic chemicals characterized by high vapor pressure at room temperature, which makes them volatile, allowing them to evaporate into the air. They come in lots of common products, such as in paints, solvents, cleaning agents, and adhesives. A few examples of common VOCs include benzene, formaldehyde, and toluene.
Why is VOC Testing Important?
Short-term Exposure: Exposure to VOCs can result in irritation of the eye, nose, and throat; headaches; and dizziness. Higher concentrations can increase the severity of these symptoms.
Long-term Exposure: Many VOCs pose a greater health risk in extended exposures. These may include damage to the liver and kidneys, effects on the central nervous system, and even cancer.
Materials of Construction: The building material, furnishings and finishes off-gas VOCs which impact indoor air quality.
Contamination Detection: The testing identifies sources of indoor air pollution in the premises so that remediation actions can be conducted on time and maintenance of quality air implemented.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have regulations and guidelines concerning indoor air quality and VOC levels. Testing helps ensure compliance with these standards.

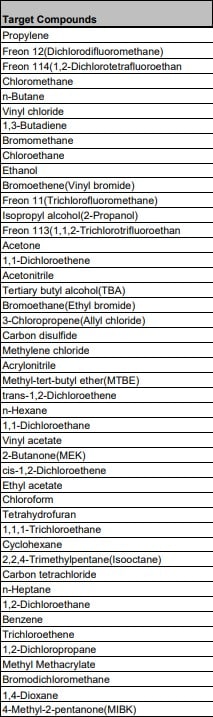
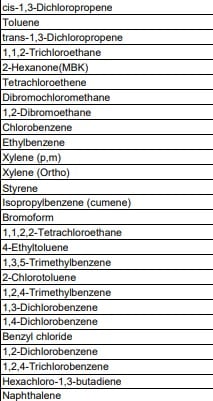
VOC Testing Methods
Pump-Based Sampling: Uses a pump to draw air through a collection device, such as a charcoal tube or canister, which is then analyzed in a laboratory.
Real-Time Monitoring: Makes use of sensors and equipment to provide minute-by- minute measurement of the concentrations of VOC in the air.
Diffusion Tubes: The air passes through a tube with a chemical adsorbent, which captures the VOCs for later laboratory analysis.
Photoionization Detectors (PIDs): Directly measures the ionization of VOCs in the air and gives readings in real time. c
Gas Chromatography: An analytical method by which different VOCs that are present in a sample are separated and identified.
Understanding of VOC Testing
Identify Potential Hotspots: A location is identified with a suspicion of VOCs usually in areas adjacent to new construction, renovation work, or of areas with heavy use of chemical products.
Method Selection: Appropriate sampling techniques would be selected by considering requirements and test conditions for a particular parameter in the environment.
Sample Collection: Follow proper procedures to ensure accurate and representative samples are collected.
Laboratory Testing: The samples collected would be taken to a certified laboratory for detailed analysis.
Direct Results: Monitoring of VOC levels and trends with the aid of direct-reading instruments.
Result Interpretation: Comparison of test results against standards set by safety and guidance.
Action Determination: Based on results, decide on action to reduce VOC levels for better air quality.
Source Elimination: Sources that emit VOCs should be eliminated.
Ventilation: Improved ventilation systems shall ensure that indoor VOC concentrations are minimized.
Only products that are either low-VOC or VOC-free shall be used in the future.
Indoor air management and a healthy living or working environment necessitate VOC testing. Identify the source of VOCs and mitigate them to reduce health risks and improve air quality. Schedule an appointment today with Quest Mold & Asbestos Inspections & Testing.

